Joint pain is a common ailment that affects people of all ages and backgrounds. It can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, making even simple tasks challenging. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and remedies for joint pain.
Joints are the connections between two or more bones in our body. They allow us to move our limbs and perform various activities such as walking, running, and bending. Without healthy joints, our body would become stiff and immobile.
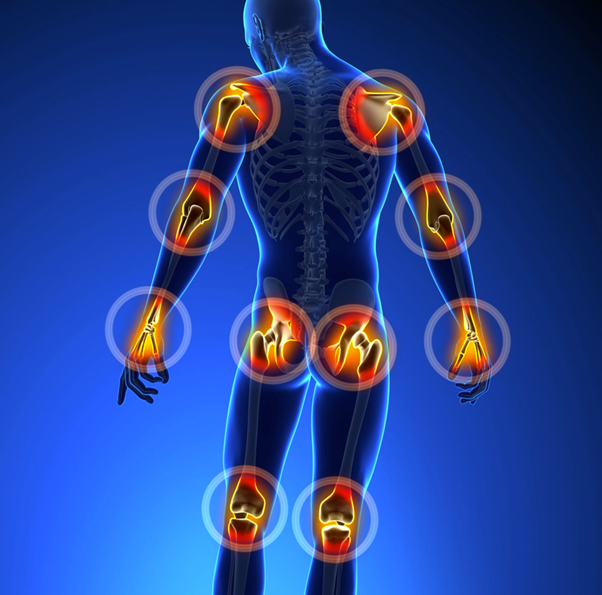
Causes of Joint Pain
Several factors can contribute to joint pain. Understanding these causes is essential to finding the right treatment and relief. Here are some common causes of joint pain:
- Arthritis: Arthritis is a group of conditions that cause inflammation and damage to the joints. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are the two most common types of arthritis. Osteoarthritis occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of your bones wears down over time, leading to pain and stiffness. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that causes the body’s immune system to attack its joints.
- Injuries: Accidents or sports injuries can damage the structures within the joint, leading to pain and discomfort. Ligament sprains, muscle strains, and fractures are some examples of joint injuries.
- Overuse: Repeatedly using a joint, especially in activities that put stress on it, can lead to overuse injuries. This is common in athletes and people with physically demanding jobs.
- Infections: Infections in the joint can cause inflammation and pain. These infections can be bacterial or viral.
- Gout: Gout is a form of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. It often affects the big toe and can cause sudden and severe joint pain.
- Other medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as lupus, fibromyalgia, and bursitis, can also lead to joint pain.
Symptoms of Joint Pain
Joint pain can manifest in various ways, depending on its cause and severity. Common symptoms include:
- Pain: The most obvious symptom of joint pain is discomfort or pain in the affected joint. This pain can range from mild to severe and may be constant or intermittent.
- Swelling: Inflammation often accompanies joint pain, leading to swelling around the affected joint. This swelling can make the joint appear red and feel warm to the touch.
- Stiffness: Joint stiffness can make it difficult to move the affected joint. It is particularly common in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
- Decreased range of motion: Joint pain can limit your ability to move the affected joint fully. This can impact your ability to perform daily activities.
- Weakness: Muscles around the painful joint may weaken over time due to disuse, which can further contribute to joint pain.
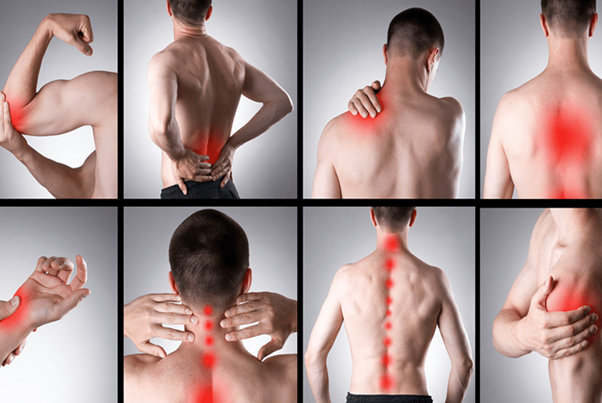
Remedies and Treatments
The treatment of joint pain depends on its cause and severity. Here are some common remedies and treatments that can help alleviate joint pain:
- Rest: Giving the affected joint adequate rest is essential, especially if the pain is due to an injury or overuse. Avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain can aid in the healing process.
- Ice and Heat: Applying ice packs can help reduce inflammation and numb the area, providing relief from pain. Heat therapy, such as warm compresses or heating pads, can help relax muscles and improve blood flow to the joint.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation. However, it’s essential to use these medications under a doctor’s guidance, especially for long-term use.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can design an exercise program to strengthen the muscles around the affected joint, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce stress on weight-bearing joints, such as the knees and hips. Losing excess weight, if necessary, can alleviate joint pain.
- Assistive Devices: Joint pain may require the use of assistive devices like canes, braces, or splints to support and protect the affected joint.
- Medications for Specific Conditions: If the joint pain is caused by a specific condition like rheumatoid arthritis or gout, your doctor may prescribe disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologics, or other medications to manage the underlying condition.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections can provide temporary relief from joint pain and inflammation. Hyaluronic acid injections can help lubricate and cushion the joint, particularly for osteoarthritis.
- Surgery: In severe cases or when conservative treatments are ineffective, surgery may be necessary. Joint replacement surgery, such as knee or hip replacement, can restore function and reduce pain.
Preventing Joint Pain
While some causes of joint pain are beyond our control, there are steps we can take to reduce the risk of developing joint pain:
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Eat a balanced diet, engage in regular physical activity, and manage stress to keep your joints and overall health in good shape.
- Avoid Overuse: If you have a physically demanding job or participate in sports, take breaks, and use proper techniques to avoid overusing your joints.
- Protect Your Joints: Wear protective gear during sports or activities that carry a risk of injury, such as helmets, knee pads, and elbow pads.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to any early signs of joint pain and seek medical attention promptly to prevent worsening conditions.
Conclusion
Joint pain is a common problem that can affect anyone, regardless of age or lifestyle. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for joint pain is crucial for managing and alleviating this discomfort. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, seeking prompt medical attention, and following the guidance of healthcare professionals, you can take steps to prevent and manage joint pain effectively, allowing you to lead a more comfortable and active life.
References:
- CDC. Joint Pain And Arthritis. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/arthritis/pain/index.htm
- Mayoclinic. Joint Pain. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/joint-pain/basics/causes/sym-20050668
- NHS. Joint Pain. Retrieved from https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/joint-pain/
